BRICS: A New Era of Economic Collaboration and Global Influence
Introduction
In an increasingly interconnected and rapidly changing global landscape, the BRICS alliance—comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa—has emerged as a formidable force in international relations and economics. Originally formed as a group of major emerging economies, BRICS represents a significant portion of the world's population, land area, and economic output. As of 2023, BRICS nations account for approximately 31% of global GDP and about 42% of the world's population, marking them as key players in shaping global economic policies and trends.
The importance of BRICS transcends mere statistics; it embodies a shift in power dynamics from traditional Western dominance to a more multipolar world order. As these nations strive for greater influence, they challenge established norms and institutions, advocating for reforms that reflect their interests. This blog aims to provide a detailed analysis of BRICS, exploring its significance in the global economy, the challenges it faces, and its prospects for the future.
Overview of BRICS
Formation
The origins of BRICS can be traced back to the early 2000s when economist Jim O'Neill coined the term to highlight the economic potential of Brazil, Russia, India, and China. The formal cooperation began in 2009 with the first summit held in Yekaterinburg, Russia, where the leaders of these nations discussed their aspirations for collaboration on various issues. The inclusion of South Africa in 2010 was a strategic move to enhance the group's influence in Africa and further diversify its membership.
Objectives
BRICS was established with several key objectives that reflect the aspirations of its member countries:
- Economic Growth: One of the primary goals of BRICS is to foster economic collaboration among its members. This collaboration aims to enhance trade, investment, and economic development, thereby boosting the economies of the member nations.
- Political Cooperation: BRICS seeks to enhance political dialogue and cooperation among member countries to promote mutual interests and support each other in global forums. This includes advocating for reforms in international institutions that better represent the interests of emerging economies.
- Cultural Exchange: The alliance also focuses on promoting cultural understanding and exchanges among its members. This objective aims to deepen the connections between the diverse populations of BRICS nations, fostering goodwill and mutual respect.
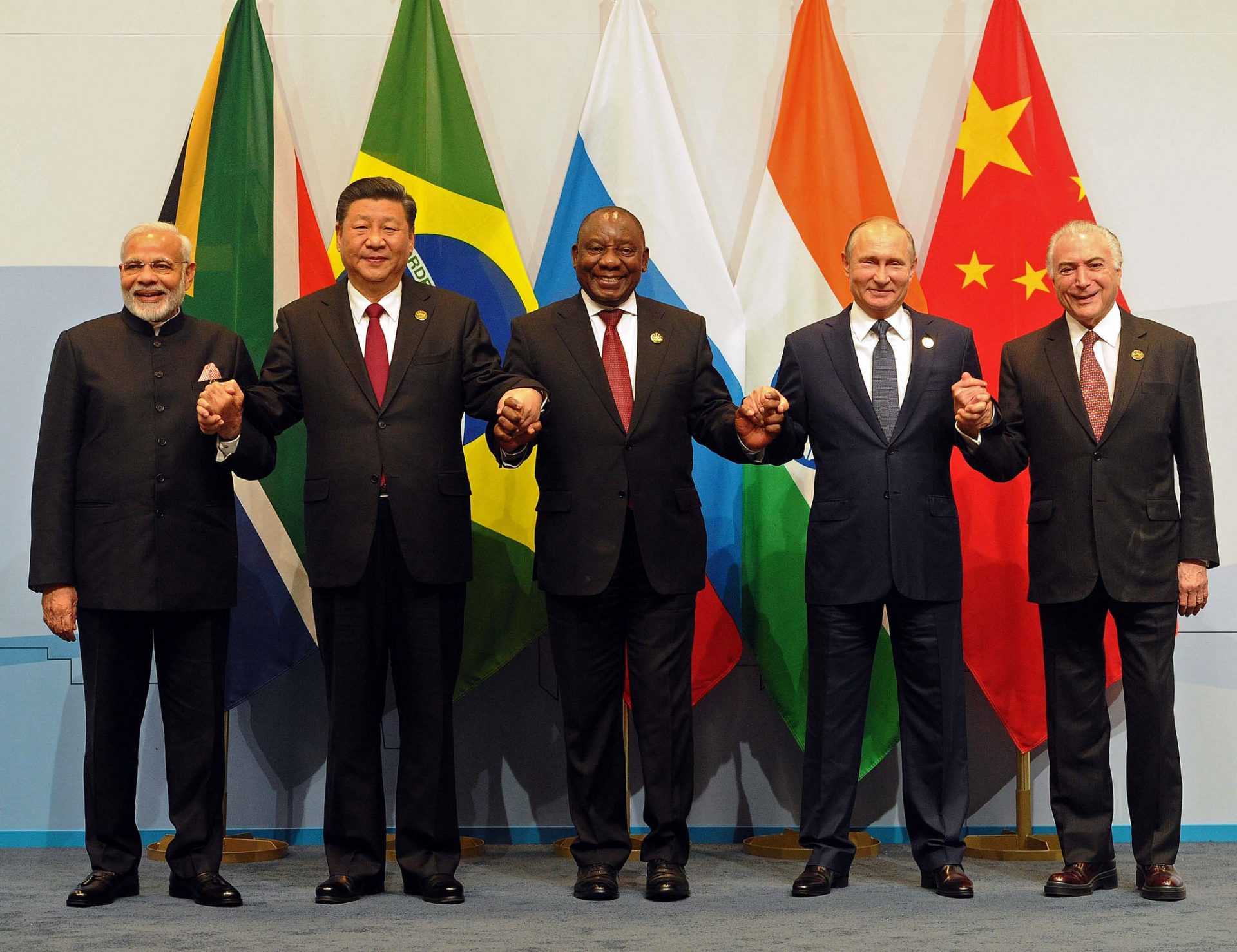

Member States
Each BRICS member state has unique characteristics that contribute to the alliance's strength:
- Brazil: As the largest country in South America, Brazil is known for its vast natural resources and agricultural output. Its GDP is approximately $2 trillion, and it is a major exporter of commodities such as soybeans, iron ore, and coffee. Brazil's economy is characterized by a mix of agriculture, services, and manufacturing, with a growing emphasis on technology and innovation.
- Russia: Rich in natural resources, particularly oil and gas, Russia plays a crucial role in the global energy market. With a GDP of around $2 trillion, the Russian economy relies heavily on energy exports, which account for a significant portion of government revenue. Additionally, Russia's strategic geopolitical positioning enhances its influence within BRICS.
- India: With a GDP of about $3 trillion, India is one of the fastest-growing major economies in the world. It boasts a diverse economic structure that includes technology, manufacturing, and agriculture. India's young and dynamic population presents opportunities for innovation and growth, making it a key player in BRICS.
- China: As the world's second-largest economy, China has a GDP of approximately $17 trillion. The country has experienced rapid industrialization and urbanization over the past few decades, driven by manufacturing, exports, and a focus on technological advancement. China's economic model and Belt and Road Initiative have significant implications for BRICS and global trade.
- South Africa: The most industrialized nation in Africa, South Africa has a GDP of about $350 billion. Its economy is diverse, with key sectors including mining, manufacturing, and services. South Africa's membership in BRICS provides a platform for the country to advocate for African interests and enhance its global standing.
Economic Significance
Collective GDP
As a bloc, BRICS nations possess considerable economic power, with a combined GDP that reached approximately $24 trillion in 2023. This figure represents around 31% of global GDP, underscoring the group's influence in international economic discussions. The economic weight of BRICS enhances its bargaining power in global negotiations, allowing member states to advocate for policies that align with their interests.
Economic Growth Rates
Historically, BRICS nations have demonstrated higher growth rates compared to traditional economic powers, particularly the G7 countries. While the G7 has seen sluggish growth rates averaging around 1-2% annually, BRICS nations have consistently achieved growth rates between 5-7%. This rapid growth can be attributed to factors such as population growth, urbanization, and industrialization, which drive demand for goods and services.
For instance, in recent years, India has emerged as one of the fastest-growing major economies, with growth rates often exceeding 7%. China, while experiencing a slowdown from its previous double-digit growth rates, remains a global economic powerhouse, contributing significantly to global trade and investment.
Trade Volume
Intra-BRICS trade has experienced remarkable growth, increasing from $25 billion in 2010 to over $200 billion in 2023. This surge reflects a concerted effort among member countries to enhance economic ties, reduce dependence on Western markets, and foster economic self-reliance. The establishment of the New Development Bank (NDB) in 2014 further facilitates trade and investment among BRICS nations, providing financial support for infrastructure projects and development initiatives.
Investment Opportunities
BRICS countries offer diverse investment opportunities across various sectors. Key areas attracting investment include:
- Technology and Innovation: Countries like India and China have become global leaders in technology and innovation, with burgeoning start-up ecosystems. Sectors such as information technology, artificial intelligence, and e-commerce present lucrative investment prospects.
- Natural Resources: Brazil and Russia, with their vast reserves of natural resources, are attractive for investments in energy, mining, and agriculture. The demand for commodities is expected to grow, especially in emerging markets.
- Manufacturing: With rising labor costs in traditional manufacturing hubs, BRICS nations like India and Vietnam are becoming preferred destinations for manufacturing, driven by favorable demographics and government initiatives.
Political Dynamics
Diplomatic Relations
BRICS nations engage in regular dialogues to address shared interests and challenges. The annual BRICS summits serve as a platform for leaders to discuss a wide range of issues, including economic cooperation, security concerns, and global governance reforms. These meetings foster diplomatic relations and enable member states to present a united front on various international issues.
Global Governance
BRICS plays a crucial role in advocating for reform in global governance institutions such as the United Nations, International Monetary Fund (IMF), and World Bank. Member nations seek to increase their representation and influence within these bodies, reflecting the changing global power dynamics. For example, BRICS has called for reforms in the UN Security Council to give more representation to developing countries, aligning with their interests in global governance.
Geopolitical Influence
The BRICS alliance serves as a counterbalance to Western political and economic influence, particularly that of the United States and the European Union. By presenting a united front on various issues, BRICS countries strive to promote a multipolar world order that reflects the interests of emerging economies. This geopolitical influence is particularly evident in areas such as trade agreements, climate change negotiations, and security discussions.

Social and Cultural Aspects
Cultural Exchanges
BRICS nations have launched several initiatives to promote cultural understanding, including student exchange programs, art exhibitions, and cultural festivals. These efforts aim to strengthen ties among member countries and foster goodwill. The BRICS Cultural Festival, for example, showcases the rich cultural heritage of member nations, promoting mutual respect and understanding.
Population Demographics
BRICS countries collectively represent a young and rapidly growing population, with significant youth demographics in India and Brazil. This youth population is seen as a potential driver of economic growth, innovation, and entrepreneurship. For instance, India has one of the largest youth populations in the world, with over 600 million people under the age of 25. This demographic advantage positions India as a key player in the global economy, particularly in technology and services.
Human Development Index (HDI)
While BRICS nations exhibit substantial economic growth, disparities exist in human development. According to the Human Development Index (HDI), which measures key dimensions of human development, such as life expectancy, education, and income, member states show varying levels of development. Countries like Brazil and South Africa face significant challenges related to education, healthcare, and income inequality, which can impact overall development and social stability.
For example, South Africa has one of the highest rates of inequality in the world, with stark disparities in access to education and healthcare. Addressing these issues is crucial for fostering social cohesion and ensuring sustainable development within BRICS.
Challenges Facing BRICS
Economic Disparities
Despite the collective strength of BRICS, economic disparities among member states pose significant challenges. Countries like China and India exhibit robust economic growth, while others like South Africa face stagnation and high unemployment rates. These inequalities can hinder effective collaboration and policy formulation. For instance, the divergent economic structures of member states can complicate negotiations on trade and investment policies.
Political Differences
Diverging political ideologies and governance models create tensions within BRICS. The member states have different political systems, ranging from democracies to authoritarian regimes, leading to varied approaches to governance and international relations. For example, Russia's geopolitical actions in Ukraine have raised concerns among other members, complicating collective decision-making and cooperation.
External Pressures
BRICS faces external pressures from global economic trends, trade wars, and geopolitical tensions, particularly with Western nations. The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have implications for BRICS, as member states navigate their relationships with these major powers. Additionally, rising protectionism and nationalism in various countries can impact BRICS' ability to promote free trade and economic cooperation.
Future Prospects
Expansion of BRICS
The potential for BRICS expansion is a topic of ongoing discussion. Countries like Indonesia, Turkey, and Mexico have expressed interest in joining the alliance. An expanded BRICS could enhance its global influence and economic power, although it may also complicate decision-making processes. The inclusion of new members would require consensus among existing members, which could be challenging given the diverse interests and priorities of each nation.
Sustainability and Green Economy
BRICS countries are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainability and addressing climate change. Initiatives aimed at promoting a green economy and sustainable development are gaining traction. For instance, China has emerged as a global leader in renewable energy, investing heavily in solar and wind power. India, too, has set ambitious targets for expanding its renewable energy capacity, aiming to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based power generation by 2030.
The focus on sustainability presents opportunities for collaboration among BRICS nations, enabling them to share best practices and technological innovations. Initiatives like the BRICS Energy Research Cooperation Platform aim to enhance cooperation in the energy sector, promoting the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
Technological Innovation
Technological innovation is crucial for the future growth of BRICS. Investments in technology, artificial intelligence, and digital transformation are expected to drive economic development and enhance competitiveness on the global stage. For instance, China is investing heavily in emerging technologies, including 5G, artificial intelligence, and robotics, positioning itself as a leader in the global tech landscape.
India's thriving start-up ecosystem is another testament to the potential for technological innovation within BRICS. With a vibrant community of entrepreneurs and investors, India is emerging as a global hub for technology and innovation, attracting significant foreign investment in the tech sector.
Case Studies
China's Economic Model
China’s rapid economic transformation has positioned it as a leader within BRICS. The country’s focus on manufacturing, exports, and technology has resulted in significant GDP growth, influencing other BRICS nations to adopt similar strategies. China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has further enhanced its economic influence, facilitating infrastructure development and trade connectivity across Asia, Europe, and Africa.
The BRI presents opportunities for collaboration with other BRICS nations, as it seeks to enhance connectivity and promote economic development in participating countries. However, the initiative has also faced criticism for creating debt dependency among partner countries, raising concerns about its long-term sustainability.
India's Emerging Market
India's economic rise presents both opportunities and challenges for BRICS. With a burgeoning middle class and a focus on digital innovation, India has the potential to become a global economic leader, contributing to BRICS’ collective strength. The government's initiatives, such as "Make in India" and "Digital India," aim to boost manufacturing and technology sectors, attracting foreign investment and creating jobs.
However, India also faces significant challenges, including income inequality, unemployment, and infrastructure deficits. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring sustainable economic growth and maximizing the benefits of BRICS membership.
Russia's Resources
Russia’s vast natural resources, particularly in energy, are pivotal to BRICS' economic power. The country is one of the world's largest producers of oil and natural gas, with energy exports playing a critical role in its economy. As the world transitions to renewable energy, Russia’s ability to adapt and diversify its economy will significantly impact the bloc's overall economic health.
Moreover, Russia's geopolitical positioning allows it to play a key role in energy security discussions among BRICS members, fostering collaboration on energy-related initiatives and projects. The development of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) further strengthens Russia's ties with other BRICS nations, enhancing regional economic integration.
Conclusion
In summary, BRICS represents a powerful alliance of emerging economies with the potential to reshape the global economic landscape. Its collective strength lies in its diverse member states, significant economic output, and commitment to cooperation. However, challenges such as economic disparities, political differences, and external pressures must be addressed for BRICS to realize its full potential.
As the world increasingly moves towards a multipolar order, BRICS’ role in promoting economic growth, political cooperation, and cultural exchange will be crucial. The future of BRICS hinges on its ability to navigate internal challenges, adapt to the rapidly changing global environment, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Key Facts and Figures
- BRICS GDP: As of 2023, BRICS accounts for approximately 31% of global GDP.
- Population: BRICS nations collectively represent about 42% of the world's population.
- Trade: Intra-BRICS trade has grown from $25 billion in 2010 to over $200 billion in 2023.
- Foreign Direct Investment: BRICS countries are increasingly attracting FDI, with China leading the way.
Final Thoughts
The BRICS alliance is at a pivotal juncture in its evolution. As it navigates the complexities of global politics and economics, the collective potential of its member states remains vast. The need for unity and collaboration among these nations has never been more critical. By embracing their shared goals and addressing their challenges, BRICS can emerge as a powerful catalyst for change in the international arena, promoting a more equitable and sustainable global order.